What to Expect When Living with Chronic Back Pain: Navigating Treatment Options

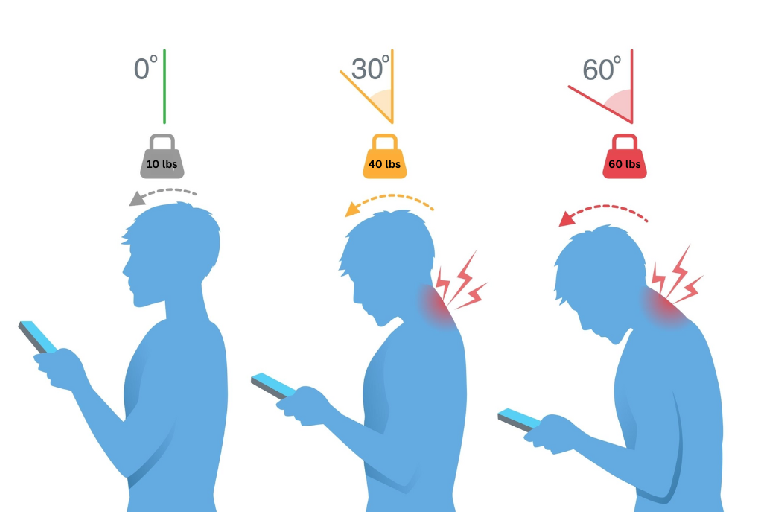
Back pain is a widespread issue affecting millions of Americans, with up to 80% of adults experience back pain at some point in their lives. Chronic back pain, described as pain lasting 12 weeks or longer, can significantly impact a person’s daily life, leading to decreased productivity, a lower quality of life, as well as the onset of other health issues.
One of the challenges faced by individuals with chronic back pain is navigating the complexities of the healthcare system, where commercial health insurance plans often dictate the course of treatment as much as the doctors. This can sometimes limit access to certain treatments or therapies that patients and healthcare providers believe would be most beneficial. It can also lead to months or years spent complying to treatment plans with little improvement and a growing sense of hopelessness.
The patient journey of someone with chronic back pain often involves multiple healthcare providers and treatments. It typically begins with conservative treatments such as physical therapy, medications, and lifestyle modifications. If these approaches are ineffective, more invasive treatments such as injections or surgery may be considered.
Physical therapy is often a key component of treatment for chronic back pain. It can help improve strength, flexibility, and mobility, which can reduce pain and improve function. Medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), muscle relaxants, and opioids may be prescribed to help manage pain. However, the long-term use of opioids for chronic pain is controversial due to the risk of dependence and addiction.
In some cases, injections such as epidural steroid injections or nerve blocks may be used to provide temporary pain relief. These injections can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain, but their effects are typically short-term and do not offer lasting relief.
Surgery is considered a last resort for chronic back pain and is usually only recommended if conservative treatments have failed to provide relief. Surgical options may include spinal fusion, laminectomy, or discectomy, depending on the underlying cause of the pain.
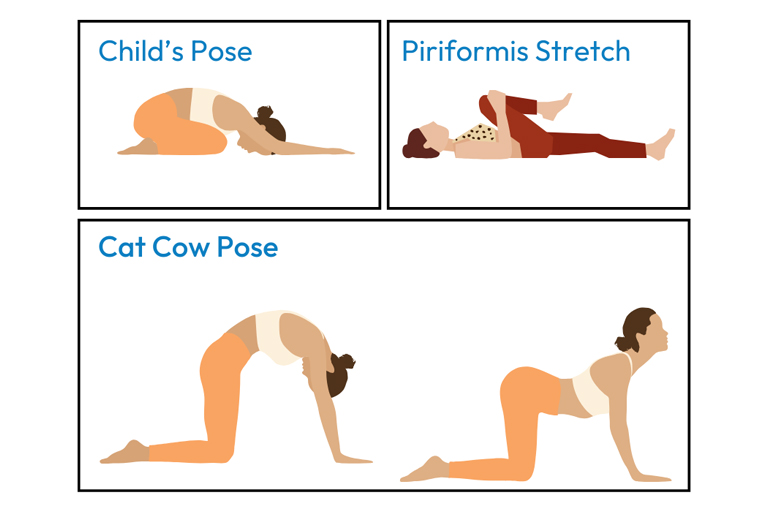
In recent years, there has been growing interest in alternative therapies such as chiropractic care, acupuncture, and mindfulness-based practices for the management of chronic back pain. These approaches focus on treating the underlying causes of pain, improving spinal alignment, and enhancing overall well-being. They also have shown to provide anywhere from 705-90% efficacy in reducing pain. By understanding the traditional trajectory of care and exploring alternative treatment options, those living with chronic back pain can take proactive steps towards managing their condition and improving their quality of life.